Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Categories:
- Rapid Thermal Anneal (RTA)
- Rapid Thermal Oxidation (RTO)
- Rapid Thermal Nitridation (RTN) (and oxynitrides)
- Rapid Thermal Diffusion (RTD)
- Rapid Thermal Chemical Vapor Deposition (RTCVD)
- Silicides and Contact formation
Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Advantages:
- Single wafer processing produces the best uniformity, especially for large wafer sizes.
- Minimize redistribution of dopants, minimal sqrt(Dt) with maximal D (high Temperature) allows repair of damage from ion implantation.
- Cold walls allow multiple processes to occur without cross contamination.
- Photochemistry can be exploited.
Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Disadvantages:
- Absolute temperatures are almost never known.
- Nonthermal-equilibrium conditions make modeling and predicting difficult.
- Uniform heating is more critical than traditional furnace processing due to high ramp rates and the resulting stress.
Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Physics
Heat Flow Mechanisms can be related to temperature rise by:
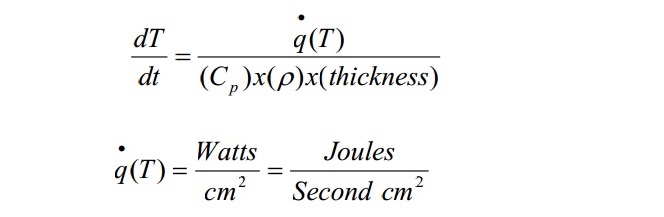
Where Cp is the specific heat (a measure of how much energy a material can absorb before it manifests in a temperature rise), r is the gram/cm3 density, and q-dot is the heat flow density (W/cm2) .
Temperature ramp rate can be enormous.
Allwin21 Corp. is the exclusive licensed manufacturer of AG Associates Heatpulse 610 Rapid Thermal Processing equipment. Allwin21 is manufacturing the new AccuThermo AW Series Atmospheric Rapid Thermal Processors and Vacuum Rapid Thermal Processors.Compared with traditional RTP systems, Allwin21″s AccuThermo AW RTPs have innovative software and more advanced temperature control technologies to achieve the best rapid thermal processing performance ( repeatability , uniformity and Stability etc.).
For many years AG Associates was the dominant manufacturer of RTP systems. It was founded in 1981 and produced the first single wafer RTP system in 1982, the Heatpulse 210. In 1987, it produced the Heatpulse 610. These RTP systems run at atmospheric pressure and rely on a pre-process nitrogen or argon purge prior to wafer processing. They are still being used around the world in manufacturing, R&D and Universities. These RTP systems have a proven track record for reliability and simplicity.
Rapid thermal processing (or RTP) refers to a semiconductor manufacturing process which heats silicon wafers to high temperatures (up to 1200 C or greater) on a timescale of several seconds or less. The wafers must be brought down (temperature) slow enough however, so they do not break due to thermal shock..Such rapid heating rates are attained by high intensity lamps process. These processes are used for a wide variety of applications in semiconductor manufacturing including dopant activation, thermal oxidation, metal reflow and chemical vapor deposition.
Rapid thermal anneal (RTA) is a process used in semiconductor device fabrication which consists of heating a single wafer at a time in order to affect its electrical properties. Unique heat treatments are designed for different effects. Wafers can be heated in order to activate dopants, change film-to-film or film-to-wafer substrate interfaces, densify deposited films, change states of grown films, repair damage from ion implantation, move dopants or drive dopants from one film into another or from a film into the wafer substrate. Rapid thermal anneals are performed by equipment that heats a single wafer at a time using lamp based heating that a wafer is brought near. Unlike furnace anneals they are short in duration, processing each wafer in several minutes. Rapid thermal anneal is a subset of processes called Rapid Thermal Process (RTP).
Application of Rapid Thermal Process
Comparisons Among All Atmospheric Rapid Thermal Processing Systems


